Determining whether compensatory mechanisms are as expected
When the primary problem is with serum [HCO3-] the lungs will attempt to counter this by altering pCO2.
Conversely, if the primary problem is with the lungs and the pCO2 level, the kidneys will counter this by altering the serum [HCO3-].
However there may be concurrent problems which interfere with this adaptive response. Such a mixed acid-base disorder must be identified prior to initiating treatment.
Expected responses:
|
Metabolic acidosis |
|
|
Metabolic alkalosis |
|
|
Respiratory acidosis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
|
|
|
Note: To convert mmHg to kPa multiply by 0.1333.
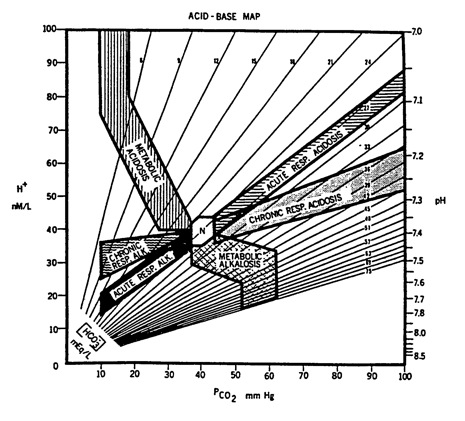
Acid-Base Map: area of normal values is labeled N; map actually extends further up than shown (to a pH of 6.6) and further to right than shown (to a pCO2 of 180 mmHg); numbered lines represent isopleths for bicarbonate (in milliequivalents per litre); from Goldberg M et al., Computer-based instruction and diagnosis of acid-base disorders: a systematic approach, JAMA 223:269-275, 1973, p. 270

If the results for your patient fall outside the marked areas, then the compensatory mechanisms are not working as expected and there is likely to be a mixed picture.