>Bartter's syndrome
|
Clinical features: |
Hypokalaemia |
Hypertrophy of the juxtaglomerular apparatus
is seen
on renal biopsy.
There is resistance to the vasoconstrictor actions of angiotensin II.
|
Causes: |
Advances in molecular
genetics have identified a number of specific abnormalities in patients with Bartter's syndrome: |
Each of these abnormalities leads to a decrease in the activity of the Na+ K+ 2Cl- cotransporter.
These sites of transporter defects are shown schematically below:
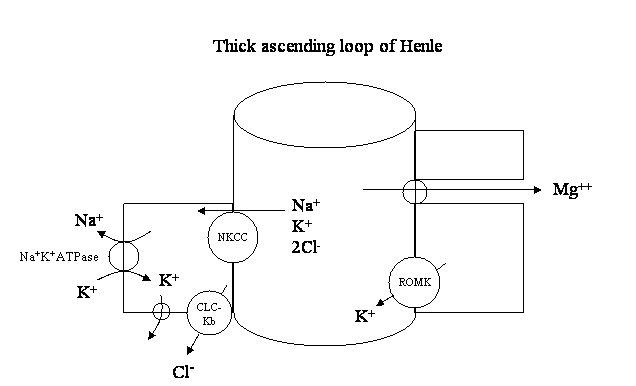
These abnormalities result in the lumen being less positively charged than normal. Cations such as magnesium, calcium and sodium are not reabsorbed as effectively resulting in hypomagnesaemia, hypercalcuria and ECF volume contraction respectively.